MySQL can be an intimidating program. All of the commands have to be
entered through a command prompt; there is no visual interface. Because
of this, having basic knowledge of how to create and manipulate a
database can save you a lot of time and headaches. Follow this guide to
create a database of US states and their populations
Creating and Manipulating a Database
-
- Create the database. From the MySQL command line, enter the command
CREATE DATABASE <DATABASENAME>;. Replace<DATABASENAME>with the name of your database. It cannot include spaces.
CREATE DATABASE us_states;
Note: Commands do not have to be entered in upper-case.
Note: All MySQL commands must end with ";". If you forgot to include the semicolon, you can enter just ";" on the next line to process the previous command.
- Create the database. From the MySQL command line, enter the command
-
- Display a list of your available databases. Enter the command
SHOW DATABASES;to list all of the databases you have stored. Besides the databse you just created, you will also see amysqldatabase and atestdatabase. You can ignore these for now.
- Display a list of your available databases. Enter the command
-
- Select your database. Once the database has been created, you will need to select it in order to begin editing it. Enter the command
USE us_states;. You will see the messageDatabase changed, letting you know that your active database is nowus_states.
- Select your database. Once the database has been created, you will need to select it in order to begin editing it. Enter the command
-
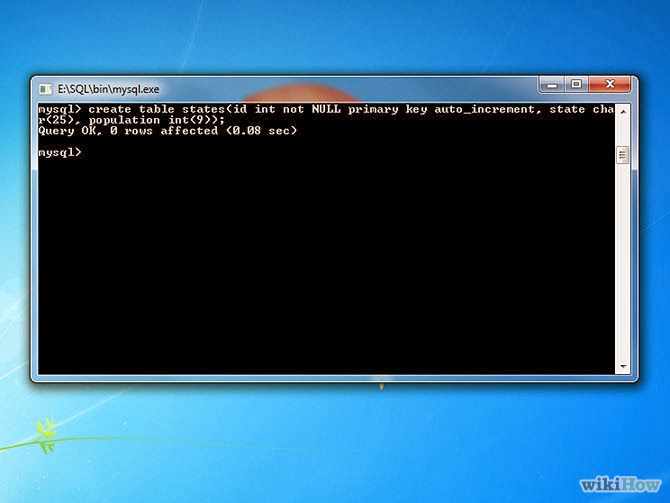
- Create a table. A table is what houses your
database’s information. To create one, you will need to enter all of
your table formatting in the initial command. To create a table, enter
the following command:
CREATE TABLE states (id INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, state CHAR(25), population INT(9));. This will create a table named "states" with three fields:id,state, andpopulation.
- The
INTcommand will make theidfield contain only numbers (integers). - The
NOT NULLcommand makes sure that theidfield cannot be left blank. - The
PRIMARY KEYdesignates theidfield as the key field in the table. The key field should be set to a field that cannot contain any duplicates. - The
AUTO_INCREMENTcommand will automatically assign increasing values into theidfield, essentially automatically numbering each entry. - The
CHAR(characters) andINT(integers) commands designate the types of data allowed in those fields. The number next to the commands indicated how many characters or integers can fit in the field.
- Create a table. A table is what houses your
database’s information. To create one, you will need to enter all of
your table formatting in the initial command. To create a table, enter
the following command:
-
- Create an entry in the table. Now that the table has
been created, it’s time to start entering your information. Use the
following command to input your first entry:
INSERT INTO states (id, state, population) VALUES (NULL, ‘Alabama’, ‘4822023’);
- This is essentially telling the database to enter the information provided into the three corresponding fields in the table.
- Since the
idfield contains the commandNOT NULL, enteringNULLas the value will force it to automatically increment to 1, thanks to theAUTO_INCREMENTcommand.
- Create an entry in the table. Now that the table has
been created, it’s time to start entering your information. Use the
following command to input your first entry:
- Create more entries. You can create multiple entries using a single command. To enter the next three states, use the following command:
INSERT INTO states (id, state, population) VALUES (NULL, ‘Alaska’, ‘731449’), (NULL, ‘Arizona’, ‘6553255’), (NULL, ‘Arkansas’, ‘2949131’);. This will create a table that looks like the following:
- Create more entries. You can create multiple entries using a single command. To enter the next three states, use the following command:






0 comments:
Post a Comment